Local Quickstart¶
Learn how to quickly try deployKF on a local Kubernetes cluster.
Introduction¶
This quickstart will guide you through setting up a local k3d Kubernetes cluster, installing ArgoCD, and running deployKF on top of it.
Not for Production Use
This quickstart is for testing purposes only. For production use, please see the Getting Started guide.
1. Requirements¶
Ensure your machine meets the following minimum requirements:
| Resource | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| CPU Cores | 4 |
| RAM | 16 GB |
| Storage | 64 GB |
You will need to install the following dependencies:
Apple Silicon
Currently, deployKF does NOT support arm64 clusters like Apple Silicon. Furthermore, some core components don't work under rosetta emulation. Please use an x86_64 machine or cloud-instance to run this quickstart.
If you use a cloud-instance, ensure it meets the minimum requirements.
Step 1 - Install Core Dependencies
First, install these core dependencies on your macOS host:
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
| Homebrew | Install Guide |
| Docker Desktop | Install Guide |
Can I use Podman instead of Docker Desktop?
Yes. While we recommend using Docker Desktop, you may use Podman instead.
Follow these steps to configure k3d to use Podman:
- Install Podman
- Enable Podman socket:
sudo systemctl enable --now podman.socket - Link Docker socket to Podman:
sudo ln -s /run/podman/podman.sock /var/run/docker.sock
Step 2 - Configure Docker Desktop
You will need to allocate at least the following resources to Docker Desktop:
| Resource | Minimum Allocation |
|---|---|
| CPU Cores | 4 |
| Memory | 10 GB |
| Storage | 64 GB |
Step 3 - Install CLI Tools
Next, install these CLI tools on your macOS host:
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
| Bash 4.4+ | RUN: brew install bash(macOS has bash 3.2 by default) |
CLI: argocd | RUN: brew install argocd |
CLI: jq | RUN: brew install jq |
CLI: k3d | RUN: brew install k3d |
CLI: kubectl | RUN: brew install kubectl |
For example, all commands can be run in your terminal like this:
brew install bash argocd jq k3d kubectl
Step 1 - Install Core Dependencies
First, install these core dependencies on your Linux host:
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
| Docker Engine | Install Guide Note, you do not need to use Docker Desktop, Docker Engine is sufficient. |
Step 2 - Install CLI Tools
Next, install these CLI tools on your Linux host:
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
CLI: argocd | Install Guide (also on Homebrew for Linux) |
CLI: jq | Install Guide (also on Homebrew for Linux) |
CLI: k3d | Install Guide (also on Homebrew for Linux) |
CLI: kubectl | Install Guide (also on Homebrew for Linux) |
How do I use Homebrew for Linux?
An easy way to install the requirements is with Homebrew. While traditionally a macOS tool, Homebrew supports linux as well. The following commands will install brew and add it to your PATH:
# install Homebrew for Linux
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# add 'brew' to your PATH
# NOTE: reopen your shell for this to take effect
(echo; echo 'eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"') >> ~/.profile
After Homebrew is installed, you may install the requirements like this:
brew install argocd jq k3d kubectl
Step 3 - Inotify Limits
On Linux, you may need to increase your system's open/watched file limits.
- Modify
/etc/sysctl.confto include the following lines:fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1280fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 655360
- Reload sysctl configs by running
sudo sysctl -p
Step 1 - Install Host Dependencies
Install these dependencies on your Windows host:
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
| Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL 2) | Install Guide |
| Docker Desktop | Install Guide |
Step 2 - Configure WSL
Configure WSL to use our custom kernel that properly supports Kubernetes (specifically Istio).
Run these commands in PowerShell (search PowerShell in start menu):
# create a directory for custom kernels
New-Item -Path "$env:USERPROFILE\WSL2Kernels" -ItemType Directory -Force | Out-Null
# download our custom kernel
$KERNEL_VERSION = "linux-deploykf-wsl-5.15.133.1"
$KERNEL_URL = "https://github.com/deployKF/WSL2-Linux-Kernel/releases/download/${KERNEL_VERSION}/linux-deploykf-wsl"
$KERNEL_PATH = "$env:USERPROFILE\WSL2Kernels\linux-deploykf-wsl"
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "${KERNEL_URL}" -OutFile "${KERNEL_PATH}"
# set the custom kernel as the default
# NOTE: this will overwrite any existing .wslconfig file
$KERNEL_PATH_ESCAPED = ("$env:USERPROFILE\WSL2Kernels\linux-deploykf-wsl" -replace '\\', '\\')
$WSLCONFIG_CONTENT = @"
[wsl2]
kernel="${KERNEL_PATH_ESCAPED}"
"@
Set-Content -Path "$env:USERPROFILE\.wslconfig" -Value "${WSLCONFIG_CONTENT}"
# restart WSL
wsl --shutdown
Restart Docker Desktop
Now you must restart Docker Desktop to ensure it is using the new kernel.
Right-click the Docker Desktop icon in the system tray, then select Restart.
Why do we need a custom kernel?
- For context on why a custom kernel is needed, see
deployKF/deployKF#41. - To see what changes we have made to the kernel, review
deployKF/WSL2-Linux-Kernel. - Hopefully, once
microsoft/WSL#8153is resolved, we will no longer need a custom kernel.
Step 3 - Install Homebrew and Dependencies
Install Homebrew for Linux within your WSL environment.
Run these commands in an Ubuntu shell (search Ubuntu in start menu):
# install Homebrew for Linux
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# add 'brew' to your PATH
# NOTE: reopen your shell for this to take effect
(echo; echo 'eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"') >> ~/.profile
Now you can install the requirements like this:
brew install argocd jq k3d kubectl
For the rest of the guide, unless otherwise instructed, run all commands in an Ubuntu shell.
2. Prepare Kubernetes¶
deployKF can run on any Kubernetes cluster, in any cloud or local environment.
For this quickstart, we will be using the k3d command line tool which runs K3s Clusters inside Docker. K3s is an extremely lightweight Kubernetes distribution that is fully compliant with the Kubernetes API, while also being very similar to a cloud-based cluster.
Step 1 - Create a k3d Cluster
Run this command to create a local k3d cluster named deploykf:
# NOTE: this will change your kubectl context to the new cluster
k3d cluster create "deploykf" \
--image "rancher/k3s:v1.28.8-k3s1"
Can I use a different version of Kubernetes?
Yes. The --image flag allows you to specify the version of Kubernetes. You may use any version of the rancher/k3s image which corresponds to a version of Kubernetes that is supported by deployKF.
Step 2 - Wait for Cluster to be Ready
Wait until the cluster is ready before continuing, ensure all Pods are in a Running or Completed state.
Here are some ways to check the status of Pods, we highly recommend trying k9s!
You can use kubectl to check the status of all pods, in all namespaces:
kubectl get -A pods
Wait for the list of pods to look like this (STATUS column is Running or Completed):
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system helm-install-traefik-crd-q9mjn 0/1 Completed 0 1h
kube-system helm-install-traefik-2h5mn 0/1 Completed 0 1h
kube-system svclb-traefik-1d8d8195-8j89l 2/2 Running 0 1h
kube-system local-path-provisioner-76d776f6f9-pslbf 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system coredns-59b4f5bbd5-7vp9v 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system traefik-56b8c5fb5c-q4hqp 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system metrics-server-7b67f64457-qc5nt 1/1 Running 0 1h
k9s makes interacting with Kubernetes much easier by providing a text-based management interface for any Kubernetes cluster. You can install k9s from Homebrew on macOS or Linux:
brew install k9s
To check the status of all pods in all namespaces:
- Run
k9sin your terminal - Presh
shift+:to open the command prompt - (tip: pressescapeto close any prompt) - Type
podsand pressenter- (tip: presstabto autocomplete resource names) - Press
0to show all namespaces - Scroll through the list of pods and check the
STATUScolumn - Quit
k9sby pressingctrl+c
The resulting list of pods will look similar to this (see the STATUS column):
Context: k3d-deploykf <0> all <a> Attach <l> Logs <y> YAML ____ __.________
Cluster: k3d-deploykf <1> default <ctrl-d> Delete <p> Logs Previous | |/ _/ __ \______
User: admin@k3d-deploykf <d> Describe <shift-f> Port-Forward | < \____ / ___/
K9s Rev: v0.27.4 <e> Edit <s> Shell | | \ / /\___ \
K8s Rev: v1.26.4+k3s1 <?> Help <n> Show Node |____|__ \ /____//____ >
CPU: 0% <ctrl-k> Kill <f> Show PortForward \/ \/
MEM: 22%
┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── Pods(all)[7] ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ NAMESPACE↑ NAME PF READY RESTARTS STATUS CPU MEM %CPU/R %CPU/L %MEM/R %MEM/L IP NODE │
│ kube-system coredns-59b4f5bbd5-7vp9v ● 1/1 0 Running 2 26 2 n/a 38 15 10.42.0.106 k3d-d │
│ kube-system helm-install-traefik-2h5mn ● 0/1 0 Completed 0 0 n/a n/a n/a n/a 10.42.0.2 k3d-d │
│ kube-system helm-install-traefik-crd-q9mjn ● 0/1 0 Completed 0 0 n/a n/a n/a n/a 10.42.0.5 k3d-d │
│ kube-system local-path-provisioner-76d776f6f9-pslbf ● 1/1 0 Running 1 16 n/a n/a n/a n/a 10.42.0.92 k3d-d │
│ kube-system metrics-server-7b67f64457-qc5nt ● 1/1 0 Running 2↓ 40↑ 2↓ n/a 57↑ n/a 10.42.0.110 k3d-d │
│ kube-system svclb-traefik-1d8d8195-8j89l ● 2/2 0 Running 0 2 n/a n/a n/a n/a 10.42.0.90 k3d-d │
│ kube-system traefik-56b8c5fb5c-q4hqp ● 1/1 0 Running 1 69 n/a n/a n/a n/a 10.42.0.133 k3d-d │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
What else can k9s do?
For more information about the features of k9s, see the k9s documentation, or press ? to view the help menu.
Some useful features:
- When viewing a list of resources, press
/to open the search prompt - (tip: pressescapeto close any prompt) - When highlighting any resource, press
yto view its YAML - When highlighting any resource, press
dto describe it - When highlighting any resource, press
eto open avimeditor for its YAML - When highlighting a pod, press
lto view its logs - When highlighting a pod, press
sto open an interactive shell - When highlighting a secret, press
xto view its base64-decoded data
Filtering by namespace:
- Press
shift+:to open the command prompt - Type
nsand pressenter - Select the namespace you want to view and press
enter(will open list of pods in that namespace) - Press
shift+:to open the command prompt - Type the name of a resource type (e.g.
serviceorsecret) and pressenter
Note, recently viewed namespaces are given a number (e.g. 1, 2, 3), press that number to show all instances of the currently selected resource type in that namespace.
3. Prepare ArgoCD¶
deployKF uses ArgoCD to apply manifests to your Kubernetes cluster.
For this quickstart, we will use the deployKF ArgoCD Plugin which adds a special kind of ArgoCD Application that produces deployKF manifests. This allows us to define the platform using a single app-of-apps which only needs your values, and a deployKF version.
Step 1 - Verify kubectl Context
We need to ensure that our kubectl context is set to the new k3d cluster. This is so we don't accidentally install ArgoCD into the wrong cluster.
Run this command and ensure the output is k3d-deploykf (or the name of your cluster):
# get the name of the current kubectl context
kubectl config current-context
How do I change my kubectl context?
We recommend using kubectx to manage your kubectl contexts.
You may install kubectx from Homebrew on macOS or Linux:
# NOTE: the installing the 'fzf' package is optional,
# it will make 'kubectx' interactive
brew install kubectx fzf
To change your context with kubectx, run these commands:
# list all contexts
kubectx
# set the current context to 'k3d-deploykf'
kubectx "k3d-deploykf"
Step 2 - Install ArgoCD
We will now install ArgoCD (and the deployKF ArgoCD Plugin) by running a script from the deployKF repo:
# clone the deploykf repo
# NOTE: we use 'main', as the latest plugin version always lives there
git clone -b main https://github.com/deployKF/deployKF.git ./deploykf
# ensure the script is executable
chmod +x ./deploykf/argocd-plugin/install_argocd.sh
# run the install script
# WARNING: this will install into your current kubectl context
bash ./deploykf/argocd-plugin/install_argocd.sh
Step 3 - Wait for ArgoCD to be Ready
After the script completes, wait for all pods in the argocd Namespace to be in a Running state:
kubectl get --namespace argocd pods
Wait for the list of pods to look like this (STATUS column is Running):
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
argocd-notifications-controller-c4bb67f9d-vbntb 1/1 Running 0 4m52s
argocd-applicationset-controller-769d968b56-p822z 1/1 Running 0 4m52s
argocd-redis-859479cd85-6l7nk 1/1 Running 0 4m51s
argocd-dex-server-6b7ddc68db-kb2x5 1/1 Running 0 4m52s
argocd-server-558686d846-5wmn6 1/1 Running 0 4m52s
argocd-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 4m52s
argocd-repo-server-bf7c47686-dd6w5 2/2 Running 0 4m52s
4. Create ArgoCD Applications¶
The only resource you manually create is the deploykf-app-of-apps, this resource generates all the other Application resources. Think of it as a "single source of truth" for the desired state of your platform.
Step 1 - Define App-of-Apps Resource
Create a local file named deploykf-app-of-apps.yaml with the contents of the YAML below.
This will use deployKF version 0.1.5, read the sample-values.yaml from the deploykf/deploykf repo, and combine those values with the overrides defined in the values parameter.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: deploykf-app-of-apps
namespace: argocd
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: deploykf-app-of-apps
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: deploykf
spec:
project: "default"
source:
## source git repo configuration
## - we use the 'deploykf/deploykf' repo so we can read its 'sample-values.yaml'
## file, but you may use any repo (even one with no files)
##
repoURL: "https://github.com/deployKF/deployKF.git"
targetRevision: "v0.1.5"
path: "."
## plugin configuration
##
plugin:
name: "deploykf"
parameters:
## the deployKF generator version
## - available versions: https://github.com/deployKF/deployKF/releases
##
- name: "source_version"
string: "0.1.5"
## paths to values files within the `repoURL` repository
## - the values in these files are merged, with later files taking precedence
## - we strongly recommend using 'sample-values.yaml' as the base of your values
## so you can easily upgrade to newer versions of deployKF
##
- name: "values_files"
array:
- "./sample-values.yaml"
## a string containing the contents of a values file
## - this parameter allows defining values without needing to create a file in the repo
## - these values are merged with higher precedence than those defined in `values_files`
##
- name: "values"
string: |
##
## This demonstrates how you might structure overrides for the 'sample-values.yaml' file.
## For a more comprehensive example, see the 'sample-values-overrides.yaml' in the main repo.
##
## Notes:
## - YAML maps are RECURSIVELY merged across values files
## - YAML lists are REPLACED in their entirety across values files
## - Do NOT include empty/null sections, as this will remove ALL values from that section.
## To include a section without overriding any values, set it to an empty map: `{}`
##
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## argocd
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
argocd:
namespace: argocd
project: default
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## kubernetes
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
kubernetes:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## deploykf-dependencies
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
deploykf_dependencies:
## --------------------------------------
## cert-manager
## --------------------------------------
cert_manager:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## istio
## --------------------------------------
istio:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## kyverno
## --------------------------------------
kyverno:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## deploykf-core
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
deploykf_core:
## --------------------------------------
## deploykf-auth
## --------------------------------------
deploykf_auth:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## deploykf-istio-gateway
## --------------------------------------
deploykf_istio_gateway:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## deploykf-profiles-generator
## --------------------------------------
deploykf_profiles_generator:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## deploykf-opt
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
deploykf_opt:
## --------------------------------------
## deploykf-minio
## --------------------------------------
deploykf_minio:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## deploykf-mysql
## --------------------------------------
deploykf_mysql:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## kubeflow-tools
## --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
kubeflow_tools:
## --------------------------------------
## katib
## --------------------------------------
katib:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## notebooks
## --------------------------------------
notebooks:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
## --------------------------------------
## pipelines
## --------------------------------------
pipelines:
{} # <-- REMOVE THIS, IF YOU INCLUDE VALUES UNDER THIS SECTION!
destination:
server: "https://kubernetes.default.svc"
namespace: "argocd"
Step 2 - Apply App-of-Apps Resource
You will need to apply the deploykf-app-of-apps resource to your Kubernetes cluster.
You can apply the resource using either the CLI or the ArgoCD Web UI:
- Create a local file named
deploykf-app-of-apps.yamlwith the contents of the app-of-apps YAML above. - Ensure your
kubectlcontext is set to thek3d-deploykfcluster. - Apply the resource to your cluster with the following command:
kubectl apply -f ./deploykf-app-of-apps.yaml
Use kubectl port-forwarding to expose the ArgoCD Web UI on your local machine:
kubectl port-forward --namespace "argocd" svc/argocd-server 8090:https
The ArgoCD Web UI should now be available at the following URL:
Retrieve the initial password for the admin user:
echo $(kubectl -n argocd get secret/argocd-initial-admin-secret \
-o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d)
Log in with the admin user, and the password you retrieved above.
The ArgoCD Web UI will look like this (but without any applications):
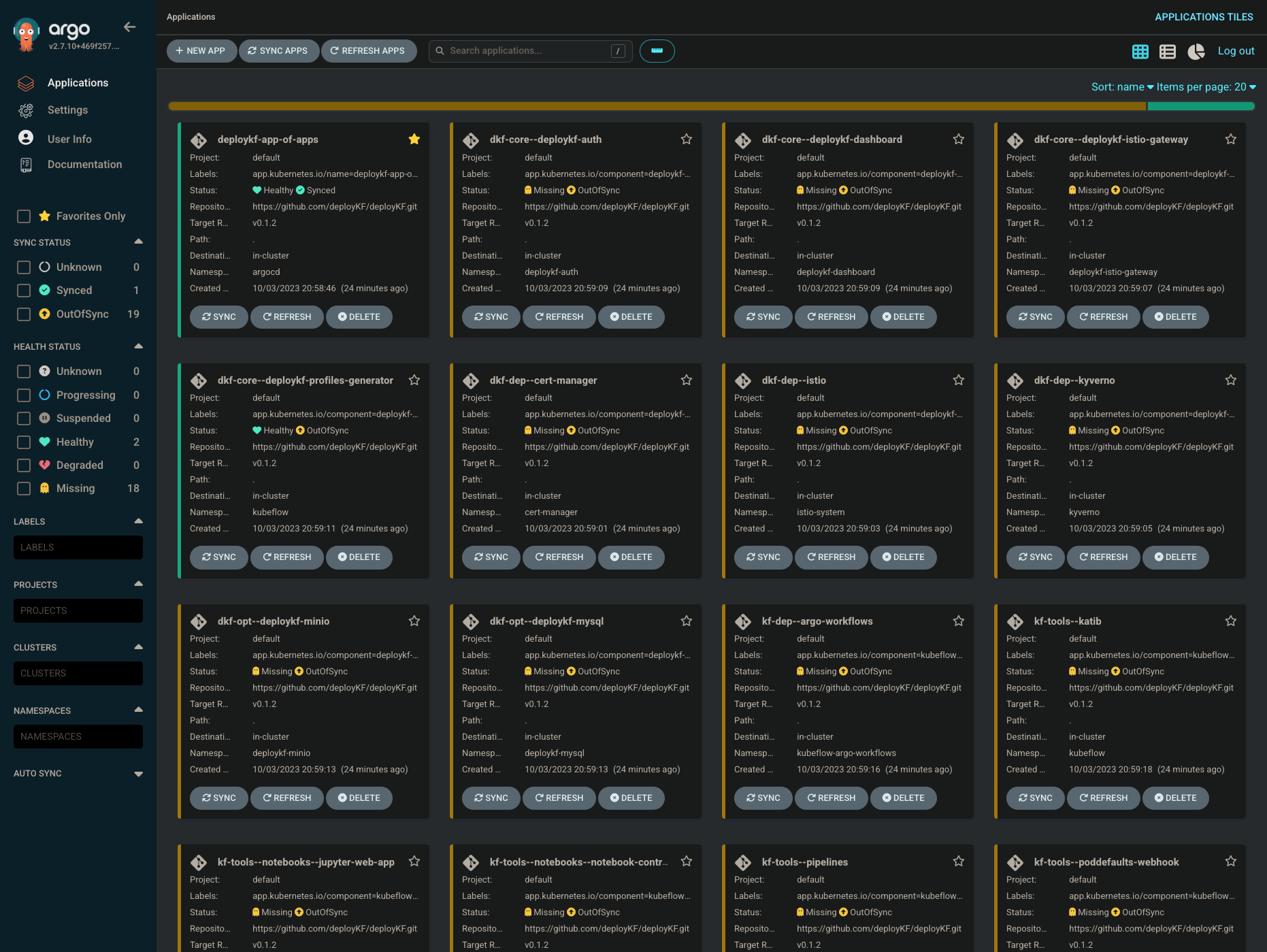
To create the app-of-apps, follow these steps:
- Click the
+ New Appbutton - Click the
Edit as YAMLbutton - Paste the application YAML into the editor
- Click the
Savebutton - Click the
Createbutton
5. Sync ArgoCD Applications¶
Now that your deployKF app-of-apps has been applied, you must sync the ArgoCD applications to deploy your platform. Syncing an application will cause ArgoCD to reconcile the actual state in the cluster, to match the state defined by the application resource.
Danger
DO NOT sync all the Applications at once!!!
The deployKF Applications depend on each other, they MUST be synced in the correct order to avoid errors. If you manually sync them all, you may need to delete your k3d cluster and start over.
For this quickstart, we will use the ArgoCD CLI via our automated sync_argocd_apps.sh script.
Step - Run the Sync Script
Run the following commands to use the sync script:
# download the latest version of the script
curl -fL -o "sync_argocd_apps.sh" \
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/deployKF/deployKF/main/scripts/sync_argocd_apps.sh"
# ensure the script is executable
chmod +x ./sync_argocd_apps.sh
# ensure your kubectl context is set correctly
kubectl config current-context
# run the script
bash ./sync_argocd_apps.sh
About the sync script
- The script can take around 5-10 minutes to run on first install.
- If the script fails or is interrupted, you can safely re-run it, and it will pick up where it left off.
- There are a number of configuration variables at the top of the script which change the default behavior.
- Learn more about the automated sync script from the
scriptsfolder README in the deployKF repo.
Please be aware of the following issue when using the automated sync script:
Bug in ArgoCD v2.9
There is a known issue (deploykf/deploykf#70, argoproj/argo-cd#16266) with all 2.9.X versions of the ArgoCD CLI that will cause the sync script to fail with the following error:
==========================================================================================
Logging in to ArgoCD...
==========================================================================================
FATA[0000] cannot find pod with selector: [app.kubernetes.io/name=] - use the --{component}-name flag in this command or set the environmental variable (Refer to https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user-guide/environment-variables), to change the Argo CD component name in the CLI
Please upgrade your argocd CLI to at least version 2.10.0 to resolve this issue.
6. Try the Platform¶
The deployKF dashboard is the web-based interface for deployKF, it gives users authenticated access to tools like Kubeflow Pipelines, Kubeflow Notebooks, and Katib.


All public deployKF services (including the dashboard) are accessed via your deployKF Istio Gateway, to use the gateway, you will need to expose its Kubernetes Service.
For this quickstart, we will be using the port-forward feature of kubectl to expose the gateway locally on your machine:
Running on a Remote Server
If you are running this quickstart on a remote server or cloud-instance (rather than your local machine), you will have to do some different steps that depend on your network setup:
Direct Network Access
If you have direct network access to the remote server (e.g. are on the same network, or VPN), make the following changes to the steps:
Step 1:
When updating the hosts file, use the IP of the remote server, rather than 127.0.0.1. For example, if the IP of the remote server is 192.168.50.15, you would update the hosts file like this:
192.168.50.15 deploykf.example.com
192.168.50.15 argo-server.deploykf.example.com
192.168.50.15 minio-api.deploykf.example.com
192.168.50.15 minio-console.deploykf.example.com
(NOTE: update the hosts file on your local machine, NOT the remote server)
Step 2:
Run kubectl port-forward on the remote server with the --address 0.0.0.0 argument, rather than your local machine. For example, you might run the following command on the remote server:
kubectl port-forward \
--namespace "deploykf-istio-gateway" \
--address "0.0.0.0" \
svc/deploykf-gateway 8080:http 8443:https
(NOTE: ensure the firewall on the remote server allows ports 8080 and 8443)
(WARNING: we don't recommend exposing the gateway to the public internet)
Step 3:
You still use the hostname set in your hosts file (NOT the IP of the remote server).
For example: https://deploykf.example.com:8443/
Over SSH Tunnel
If you do not have direct network access to the remote server, you can create an SSH tunnel.
For example, you might run the following command on your local machine to create the tunnel:
SSH_USER="user"
SSH_HOSTNAME="hostname"
ssh -N \
-L 8080:localhost:8080 \
-L 8443:localhost:8443 \
"${SSH_USER}@${SSH_HOSTNAME}"
Step 1:
As the tunnel listens on your local machine, you still use 127.0.0.1 in the hosts file.
Step 2:
Run kubectl port-forward on the remote instance, rather than your local machine. For example, you might run the following command on the remote instance:
kubectl port-forward \
--namespace "deploykf-istio-gateway" \
svc/deploykf-gateway 8080:http 8443:https
Step 3:
You still use the hostname set in your hosts file to access the dashboard.
For example: https://deploykf.example.com:8443/
Step 1 - Modify Hosts
You can't access deployKF using localhost, 127.0.0.1, or any other IP address.
Without an HTTP Host header, deployKF won't know which service you are trying to access. You must update your hosts file to resolve deploykf.example.com and its subdomains to 127.0.0.1.
Edit the hosts file on your local machine (where you run your web browser), NOT the Kubernetes cluster itself.
The /etc/hosts can ONLY be edited by a user with root privileges.
Run the following command to open the hosts file in a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
# OR: sudo vim /etc/hosts
Add the following lines to the END of your /etc/hosts file:
127.0.0.1 deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 argo-server.deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 minio-api.deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 minio-console.deploykf.example.com
The /etc/hosts can ONLY be edited by a user with root privileges.
Run the following command to open the hosts file in a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
# OR: sudo vim /etc/hosts
Add the following lines to the END of your /etc/hosts file:
127.0.0.1 deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 argo-server.deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 minio-api.deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 minio-console.deploykf.example.com
The hosts file can ONLY be edited by the Windows Administrator user.
Run this PowerShell command to start an Administrator Notepad:
Start-Process notepad.exe -ArgumentList "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts" -Verb RunAs
Add the following lines to the END of your C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts file:
127.0.0.1 deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 argo-server.deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 minio-api.deploykf.example.com
127.0.0.1 minio-console.deploykf.example.com
Step 2 - Port-Forward the Gateway
The kubectl port-forward command creates a private tunnel to the Kubernetes cluster. Run the following command on your local machine to expose the deploykf-gateway Service on 127.0.0.1:
kubectl port-forward \
--namespace "deploykf-istio-gateway" \
svc/deploykf-gateway 8080:http 8443:https
If your browser suddenly stops working, press CTRL+C to stop the port-forward, and then run the command again (kubernetes/kubernetes#74551).
Step 3 - Log In
You should now be presented with a "Log In" screen when you visit the exposed URL:
https://deploykf.example.com:8443/
Remember that you can NOT access deployKF using localhost or 127.0.0.1!
By default, there are a few static credentials set by the deploykf_core.deploykf_auth.dex.staticPasswords value:
Credentials: User 1
Username: user1@example.com
Password: user1
- This account has write access to
team-1profile. - This account has read access to
team-1-prod.
Credentials: User 2
Username: user2@example.com
Password: user2
- This account has write access to
team-1profile. - This account has read access to
team-1-prod.
Credentials: Admin (DO NOT USE - will be removed in future versions)
Username: admin@example.com
Password: admin
- This account is the default "owner" of all profiles.
- This account does NOT have access to "MinIO Console" or "Argo Server UI".
- We recommend NOT using this account, and actually removing its
staticPasswordsentry. - We recommend leaving this account as the default "owner", even with
@example.comas the domain (because profile owners can't be changed).
Step 4 - Explore the Tools
deployKF includes many tools which address different stages of the data & machine learning lifecycle:
We also provide a number of user-focused guides for these tools:
| Tool | User Guide |
|---|---|
| Kubeflow Pipelines | Access Kubeflow Pipelines API |
| Kubeflow Pipelines | GitOps for Kubeflow Pipelines Schedules |
Next Steps¶
- Build a production-ready deployKF platform!
- Join the deployKF community!
Support us with a star on GitHub!
- Get support from our experts!
Created: 2023-10-18